A new and unique technology is just around the corner, potentially changing the way we connect to the internet. It offers different benefits than traditional Wi-Fi, and while it’s too early to say what this means for broadband in our homes, it not only offers promising possibilities, but also certain limitations. What is this new technology and how does it work?
What is LiFi?
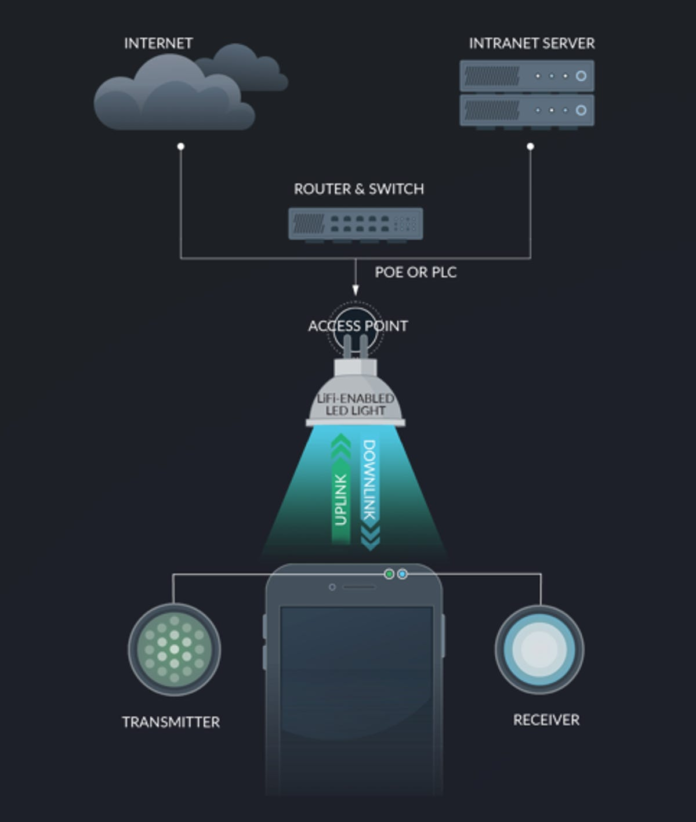
Light Fidelity, also known as Li-Fi, uses the power of light to transmit data. Unlike Wi-Fi, which uses radio waves to create a wireless connection, Li-Fi relies on light to transmit data. Through this process, Li-Fi promises speeds that are 100 times faster than Wi-Fi.
Research into Li-Fi has been around since the early 2000s. Together with his team, German physicist Harald Haas founded this technology by discovering that light can be used for two-way data transfer. It wasn’t long before the French company Oldecomm, one of the world leaders in this technology, started conducting experiments with Li-Fi in 2008. In July, Europe launched the Ariane 6 into space, conducting four experiments, one of which focused on testing Li-Fi. -Fi technology.
How does LiFi work?
Li-Fi functions as a visible light communication system; at its core, data is transferred from LED lights. These lamps carry light pulses that produce information similar to Morse code. No, this process cannot be seen with the naked eye. The game-changers in this scenario are the compatible devices that can quickly synthesize this information.
What does this mean for the internet?
Wi-Fi, also known as wireless fidelity, first emerged in 1996. In recent years, the development of technologies like Wi-Fi 6 and 6E and the introduction of Wi-Fi 7 have changed the way we stay connected.
Li-Fi transfers data faster than Wi-Fi, resulting in faster speeds. Speeds are not the only important factor in a wireless connection.
The LiFi Group, a pioneer in commercializing Li-Fi technology and its products in the digital space, highlighted other notable benefits such as increased security.
“Security is another key benefit of Li-Fi, as the signals are limited to the area illuminated by the light source and cannot penetrate walls. The risk of unauthorized access is significantly reduced,” says a spokesperson for The LiFi Group to CNET.
In terms of speeds, Li-Fi speeds can reach up to 224,000 megabits per second (in theory) and could be especially beneficial for smart cities, virtual reality, 4K streaming and even online gaming, where lower latency is crucial. Additionally, because Li-Fi does not rely on radio frequencies like Wi-Fi, your connection will be free from electromagnetic interference. Li-Fi can also be safer for your home because it produces less radiation.
It’s worth noting that this technology is still in its infancy, so we won’t see its real impact until it’s fully implemented in the real world.

I digress, while this technology isn’t perfect yet, there are some important things you should know:
Plus points
- Speed: Light sources transmit more data faster than radio waves used by Wi-Fi.
- Efficiency: Li-Fi is more energy efficient because it harnesses the power of LED lights.
- Security: Li-Fi technology reduces the risk of your data being intercepted by outside threats.
- Availability: Light sources are everywhere, increasing your chances of connecting to the Internet.
Disadvantages
- Limited range: Your connection will be limited to closed areas as this technology relies on light sources. Large establishments and companies may have a more difficult time using this technology.
- Limited compatibility: This is a newer technology, which means fewer devices are equipped to decrypt the data.
- Doesn’t fix slow internet speeds from ISPs: If you are on your provider’s slowest plan or are experiencing slower speeds, Li-Fi does not solve these problems.
Li-Fi and its limitations
According to Oldecomm, Li-Fi has many limitations: from breaking into the mainstream market to the required line of sight. As mentioned above, Li-Fi technology will be limited to small spaces, resulting in limited range. More importantly, this technology relies on line-of-sight, meaning users must always be in the presence of light signals to maintain their connection to the Internet. This would be particularly difficult for millions of Americans who use the Internet while commuting or traveling.
Where can I find Li-Fi?
Currently, Li-Fi is still in the research phase in the US and other parts of the world. It may be some time before we see what impact Li-Fi will have on the Internet. Li-Fi is expected to be rolled out to the mainstream market in the coming years. Oldecomm predicts that Li-Fi will be available sometime between 2024 and 2029. The implementation of this technology will depend solely on business investment.

Li-Fi technology would benefit many industries such as defense and government, increasing the ability to transmit data securely.
On the plus side, we may not be that far off as we see this technology in several industries. The LiFi Group describes this technology as crucial for sectors such as defense and government, which is optimal for transferring data securely. Other industries, such as aviation, are also using this technology, as seen at Spectrum Networks LLC, based in Fife, Washington.
In addition, there has been increased interest among US companies funding research to develop this technology. VLNComm, based in Charlottesville, Virginia, is a leader in VLC technology and pivotal in the development of Li-Fi. In addition, the company Signify, known for its energy-efficient lighting products, is also an important player in the field of VLC technology. This company is headquartered in the Netherlands, but the North American company is based in Bridgewater, New Jersey. Both companies are doing work that will lay the foundation for Li-Fi technology.
What’s next for LiFi?
“We have been in discussions with several leading companies, not only within the LiFi and wireless communications sector, but also in industries such as consumer electronics, automotive, telecommunications, logistics and more,” the LiFi Group spokesperson said. The demand for innovative connectivity solutions, especially in environments where traditional wireless technologies face limitations, is likely to drive more companies to explore and invest in Li-Fi in the near future.”
What is the ultimate goal of Li-Fi?
Li-Fi technology seems like a great alternative to Wi-Fi and could theoretically benefit many industries. It’s too early to say that this technology will replace Wi-Fi as a whole. It may be some time before we actually see tangible evidence of its impact on wireless connectivity. Li-Fi is promising as we see increasing interest from companies funding research to develop the standard. Until then, we will keep you informed of new developments with this technology.
What is Li-Fi Frequently Asked Questions
How is Li-Fi different from Wi-Fi?
For starters, Wi-Fi uses radio waves to create a wireless connection, while Li-Fi uses light signals to transmit data. Li-Fi offers several advantages over Wi-Fi, such as the ability to transmit more data at an accelerated rate, resulting in speeds that are 100 times faster than Wi-Fi. The main advantage of Wi-Fi is that it offers a wider range of connectivity because radio waves can pass through walls. Li-Fi, on the other hand, relies on a direct line of sight for light signals, meaning your connection is limited to enclosed spaces.
Li-Fi is already used in several industries (defense, government, medical and automotive), but the technology is still in the research phase. It is still too early to say what consequences this will have for the internet. Oldecomm expects Li-Fi to be rolled out to the mainstream market between 2024 and 2029. Keep an eye on this page for any new updates we have about Li-Fi.
What are the limitations of Li-Fi technology?
Li-Fi has its advantages, but also comes with certain limitations. Li-Fi technology has limited range and compatibility and will not solve the slow internet speeds caused by your ISPs. The biggest drawback to Li-Fi is that it relies on a direct line of sight of light signals to power your connection.