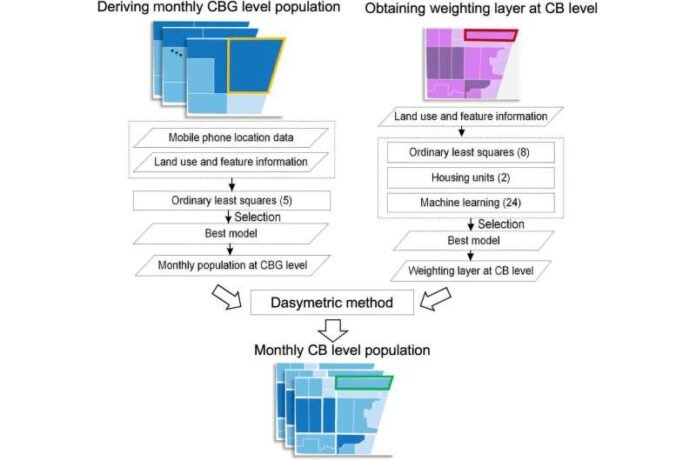
Flowchart of the proposed hybrid methodology. The number between “()” means the number of these statistical models. ‘Land use and variable information’ refers to the residential classification and population-related variables in ‘Data preprocessing’. Credit: Journal of Remote Sensing (2024). DOI: 10.34133/remotesensing.0227
The research team at SUNY Buffalo’s Department of Geography has developed an innovative framework that uses a combination of 34 models to map monthly population distributions at fine resolutions. By integrating mobile phone data, building area and detailed residential classifications, they created highly accurate population maps.
The most successful model used ordinary least squares (OLS) regression, which incorporated mobile phone location data and a classification of buildings into seven classes, such as single-family homes and mixed-use residential buildings. The model showed high accuracy (R² = 0.82) and effectively captured monthly population variations.
This approach provides a practical and replicable method for urban planners and researchers to monitor population dynamics in detail. The study was published on August 23, 2024 in the Journal of Remote Sensing.
The framework uses remote sensing orthoimage, GIS tax parcel data and SafeGraph home panel data. Remote sensing data sources, such as LiDAR and Landsat 8, were used to improve spatial detail by mapping building areas and vegetation cover. By comparing different models, the study identified building area as a key variable in population distribution. Machine learning models were also tested to further improve accuracy in predicting population trends.
“This framework provides a new solution for tracking urban population dynamics. By integrating mobile data with remote sensing, we can now create monthly population maps that are more accurate and timely, which is crucial for urban planning and disaster management,” said Le Wang, co-author of the study and professor in the Department of Geography at SUNY Buffalo.
The study used a two-step hybrid method. First, cell phone data were combined with population-related variables to update population estimates at the census block group (CBG) level. A weighted layer was then created using statistical models and machine learning techniques, refining the population data down to the census block (CB) level. Model validation used random sampling and showed high accuracy, with an R² value of 0.82.
This hybrid approach, which combines remote sensing and mobile phone data, can be applied to monitor population changes in different cities. Future applications could extend the model to larger regions and integrate additional dynamic data sources, such as real-time traffic or public service data, to further improve prediction accuracy and scalability. This could be a valuable tool for urban management, emergency response and policymaking, providing more detailed and up-to-date population insights.
More information:
Suiyuan Wang et al., A Novel Framework for Fine-Resolution Updated Population Mapping with Remote Sensing and Cell Phone Data, Journal of Remote Sensing (2024). DOI: 10.34133/remotesensing.0227
Offered by TransSpread
Quote: Framework integrates mobile and remote sensing data for population maps (2024, October 29) retrieved October 29, 2024 from https://techxplore.com/news/2024-10-framework-mobile-remote-population.html
This document is copyrighted. Except for fair dealing purposes for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for informational purposes only.