The role of the CISO continues to expand, driven by the increasing number of breaches and cyberattacks such as ransomware, as well as SEC requirements for public organizations to disclose material breaches.
Among the fastest-evolving frontiers in enterprise cybersecurity: mobile, the Internet of Things (IoT), and operational technology (OT) systems. Today, 96.5% of people access the Internet with a mobile device, while 59% of Internet traffic is generated by mobile devices. Meanwhile, OT and cyber-physical systems, once siled and isolated from the internet, have quickly become integrated into corporate networks, where threats can spread.
To shed light on this growing threat landscape, the Zscaler ThreatLabz research team conducted a detailed analysis of mobile and IoT/OT attack trends from June 2023 to May 2024.
Overall, ThreatLabz has tracked a rise in financially motivated mobile attacks – with 111% growth in spyware and 29% growth in banking malware – most of which can bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA). Meanwhile, IoT attacks grew 45% year-over-year and ThreatLabz identified pervasive security risks in OT environments.
Below we summarize the key findings from the report. For comprehensive insights into mobile and IoT/OT trends, case studies and best practices to secure your organization, download the Zscaler ThreatLabz 2024 Mobile, IoT and OT Threat Report.
Top trends in mobile and IoT/OT
- Increase in financially motivated mobile threats, including a 111% increase in spyware and 29% growth in banking malware.
- Despite an overall decline in Android attacks, financially motivated mobile threats are growing, with the majority able to bypass MFA.
- IoT attacks increased by 45% based on blocked attempts in the Zscaler cloud compared to our 2023 report.
- Zscaler blocked 45% more IoT malware transactions than the year before. ThreatLabz also noted a 12% increase in attempts to send malware (payload deliveries) to IoT devices.
- ThreatLabz discovered more than 200 fake apps on the Google Play Store.
- This includes Anatsa, a well-known Android banking malware that has targeted more than 650 financial institutions by using PDF and QR code readers to spread itself.
- Older and end-of-life operating systems (OS) make OT systems vulnerable.
- OT and cyber-physical systems, previously disconnected and isolated from the Internet, are quickly becoming integrated into corporate networks, allowing threats to spread.
- In an analysis of large-scale OT deployments, ThreatLabz found that 50% or more of OT systems are running an end-of-life operating system, many with known vulnerabilities. Meanwhile, high-risk protocols and services abound in east-west OT traffic.
Top goals for mobile and IoT/OT
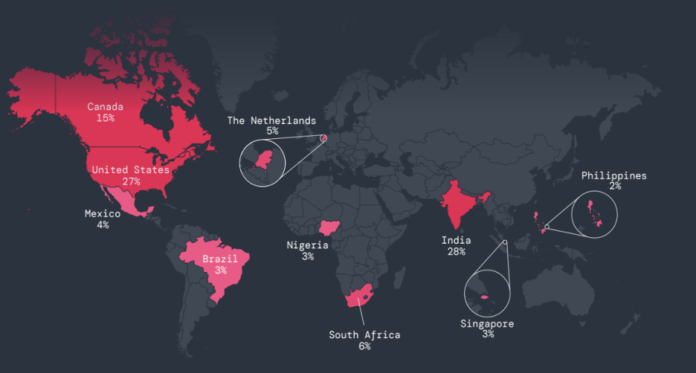
5. India was the top target for mobile attacks, receiving 28% of all attacks, followed by the US, Canada, South Africa and the Netherlands. The United States remains the top target of IoT attacks, with 81% of all attacks, followed by Singapore, Great Britain, Germany and Canada.
Zscaler
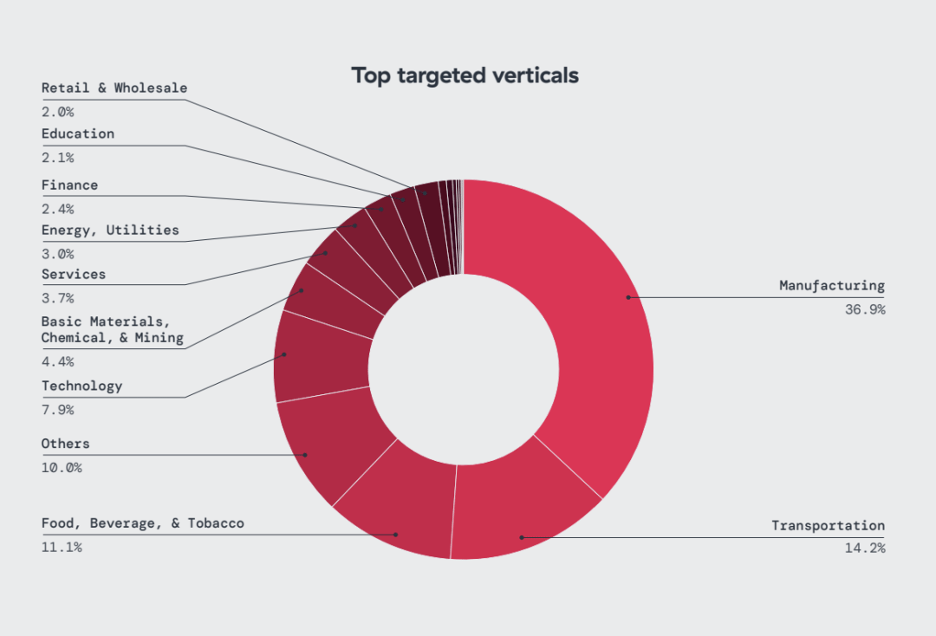
6. Industry had the highest number of IoT attacks, accounting for 36% of all observed IoT malware blocks, followed by transportation (14%) and food, beverage and tobacco (11%). The technology and education sectors were the most targeted by mobile threats.
Zscaler
Mobile, IoT and OT security without trust
As cyber attacks targeting mobile and IoT/OT assets become more sophisticated, companies need a way to reduce cyber risk while embracing IoT and OT connectivity to drive business. Not only are IoT attacks growing, but threat actors are actively targeting OT devices and critical infrastructure, which CISA has warned about. Meanwhile, enterprises need a way to robustly secure mobile connectivity to any SaaS or private application, whether in the cloud or in the data center. To protect these devices and systems, companies must adopt a zero trust approach that mitigates cyber threats and improves their security posture:
- Discover, classify and inventory IoT and OT assets: Work to gain full visibility into your IoT and OT attack surface; this includes discovering, classifying, and inventorying both managed and unmanaged or “shadow” devices. With this kind of holistic view, defenders can prioritize their efforts, identify key vulnerabilities, and develop a proactive approach to securing these assets.
- Enable zero trust connectivity: Leverage a robust zero trust architecture that enables adaptive access decisions based on the real-time security and posture of user devices, risk factors and device telemetry, ensuring secure direct connectivity between endpoints and applications – never to the underlying network.
- Enforce zero trust device segmentation: Apply least privilege access controls for device-to-application, user-to-application, and application-to-application segmentation. This granular level of segmentation eliminates lateral movements, minimizes data exposure, and strengthens your overall security posture by reducing the chance of a single compromised device compromising the entire network. This should include isolating and fully segmenting agentless IoT/OT devices into a secure “network of one,” including legacy servers and headless machines.
- Ensure a consistent zero trust security policy: Ensure zero trust access policies are consistently enforced across all environments, whether users are at headquarters, brand locations, or accessing applications remotely.
As mobile and IoT/OT threats become more common, it is critical that you understand the latest trends, the implications of these types of attacks, and the best-practice strategies you can implement to protect your organization against an entire series of threats.
Get your copy of the Zscaler ThreatLabz 2024 Mobile, IoT and OT Threat Report today.